Spinal Stenosis
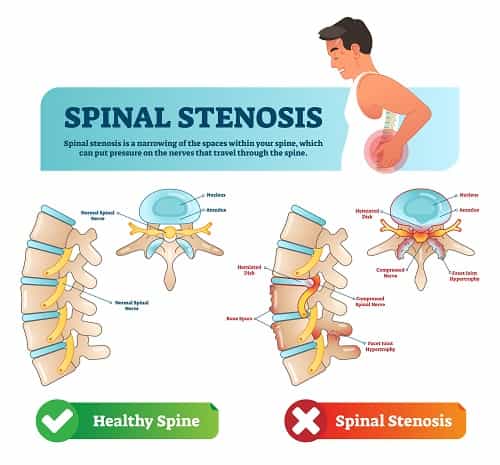
What Is Spinal Stenosis?
When we talk about spinal stenosis, we are essentially referring to a condition in which the spinal canal becomes narrower and there is a reduced amount of space for the nerves. This can cause the spinal cord or nerves to become compressed or pinched, which can cause pain and other problems. This condition typically sets in as a result of acquired degenerative changes.
Think of the intervertebral disc as the tire of a car which gets deflated and sags over a period of time. When this happens, there is an overall loss of height to the spinal front. Also, the facet joints located at the back begin taking a greater amount of load. This ultimately results in the degeneration of the facet joint and the ligaments and joints might get inflamed and enlarged.
Spinal stenosis can happen in the lower back area (most common) and neck area.
What causes spinal stenosis?
- Herniated disks
- Bone spurs
- Aging
- Spinal osteoarthritis
- Spinal fractures and injuries
- Congenital spinal stenosis
- Spinal injuries
- Spinal tumors
- Degenerative disc
- Thickened ligament
- Spinal deformity
What are the symptoms of spinal stenosis?
As the spinal canal starts to become narrower which is a slow process, the patient may or may not have any symptoms at first.
Symptoms of lower back spinal stenosis:
- Pain in the lower back.
- Sciatica.
- Radicular pain that spread from your spine into your legs.
- Numbness and stiffness in the buttocks or leg.
- Weakness in the leg or foot.
- Pain when standing for long periods or walking. Sitting down would normally help relieve the pain.
- Loss of bladder or bowel control.
- Foot drop.
- Coming and going pain – not continuous.
Symptoms of neck spinal stenosis:
- Neck pain.
- Numbness or weakness in the arm, hand, leg or foot.
- Balance problem.
- Loss of hand functions such as writing.
You should consult a doctor if you experience any of the symptoms listed above.
How is spinal stenosis diagnosed?
- Medical history review.
- Analyse your symptoms.
- Curry out physical examination.
- X-rays, MRI or CT scans.
- Electromyelogram (for spinal nerves).
- Bone scan (spine condition).
What are the treatments for spinal stenosis?
We normally start with non-surgical treatments such as physical therapy, medication or epidural injections. If these treatments do not relieve the pain, we may consider surgical treatment.
Medication Types:
- Over the counter pain relief medication such as aspirin and ibuprofen.
- Antidepressants.
- Opioids.
- Muscle relaxants.
- Anti-seizure medication.
- Corticosteroid steroid injections.
- Anesthetics.
Surgical treatment can include the following:
- Laminectomy – removing part of the vertebrae to provide more space for the nerves.
- Foraminotomy – widening the part of the spine where the nerves exit.
- Spinal fusion – using metal implants to attach the affected spine bones together.
- Laminotomy – removing part of the vertebrae to relieve pressure.
- Decompression procedure – Use of needle-like instruments to remove part of the thickened ligaments in your spinal column.
- Laminoplasty – reconstructs the vertebral lamina to relieving pressure on the spinal cord.
- Interspinous process spaces – removing part of the lamina and spacers are inserted between the spinous processes which are the bones that extend off the back of each vertebrae.

